Linear Circuit Lab (2) – Electronic Circuits Lab
Description
Brand: PValley
Model: HP-76LS8
Country of Origin: China
Features:
- Ideal for electronic circuit experiments and designing exercises
Integrated experimental circuit and trainer with comprehensive experiment curriculum - Supply complete training device easy and effective for experiments
- With universal breadboard for circuit designing and prototypes
- All modules equipped with an 8-bit DIP switch for fault simulations
- Individual keeping case for all modules easy carrying and storage facilities
General Specification:
Body Material:
Hard Round support board or Plastic Sheet
Sheet Type: Digital
Country of origin: Pakistan
Feature:
- Sheet thickness 6 mm
- Two-Part Combination(Transparent/white)
- UV Printout
Protection System
Feature:
- Safety tripping
- Low insertion loss and high reliability
Panel Box
Brand: Madhav Enterprise
Country of origin: Indian
Features:
- Shape: Rectangular
- Surface Finish: Smooth
- High quality raw material
Best structure
Brand: Altech
Country of origin: Bangladesh
Feature:
- Sheet thickness 5mm
- Square Shape
Power Supply
Brand: Fexcon
Country of origin: China
Feature:
- Output Voltage 5VDC
- Output Current 10000 mA
- Power Nature
- Input Voltage (100-250)VAC
Power Monitoring
Brand: UNI-T
Country of origin: China
Feature:
- Self-operating voltage 5V
- Self-Consumption Current 2500 mA
- Power Nature
- Two-row for Voltage & Current
Use Connector
Brand: ZHT
Country of origin: China
Feature:
- Banana Female Connector Diameter 4 mm
- Banana Male Connector Diameter 2mm
Working area:
- Working area: 40*24 inch
Technical Specifications:
- Main Unit
- DC Power Supply
(1) Fixed DC power supply
- Voltage range : ±5V, ±12V
b. With output overload protection
(2) Dual DC power supply
- Voltage range : ±3V ~ ±18V, continuously adjustable
b. With output overload protection
- AC Power Supply
(1) Voltage range : 9V ~ 0 ~ 9V
(2) With output overload protection - Function Generator
(1) Output waveform : sine, square and triangle
(2) Output frequency : 10Hz ~ 100KHz, 4 settings, continuously adjustable
(3) Accuracy : ±5% of full scale value
(4) Output impedance : 50 ohms
(5) Output voltage : ≥ 18Vpp (open loop), ≥ 9Vpp (with 50 ohms load) - 3 1/2 digit Digital Voltmeter/Ammeter
(1) DC voltage range : 2V, 200V
(2) DC voltage accuracy : ±0.3% of reading + 1-digit
(3) DC current range : 200µA, 2000mA
(4) DC current accuracy : ±0.5% of reading + 1-digit - Analog Meters
(1) AC current : 0 ~ 100mA ~ 1A
(2) AC voltage : 0 ~ 15V
(3) DC current : 0 ~ 100mA ~ 1A
(4) DC voltage : 0 ~ 20V - Speaker : 8 ohms, 0.25W speaker with driver circuit
- Variable Resistors
(1) 1K ohms, 0.25W variable resistor with 3 terminals (A,B,C)
(2) 10K ohms, 0.25W variable resistor with 3 terminals (A,B,C)
(3) 100K ohms, 0.25W variable resistor with 3 terminals (A,B,C)
(4) 1M ohms, 0.25W variable resistor with 3 terminals (A,B,C) - Breadboard: 1680 tie-point breadboard on top panel can be easily put into and taken off.
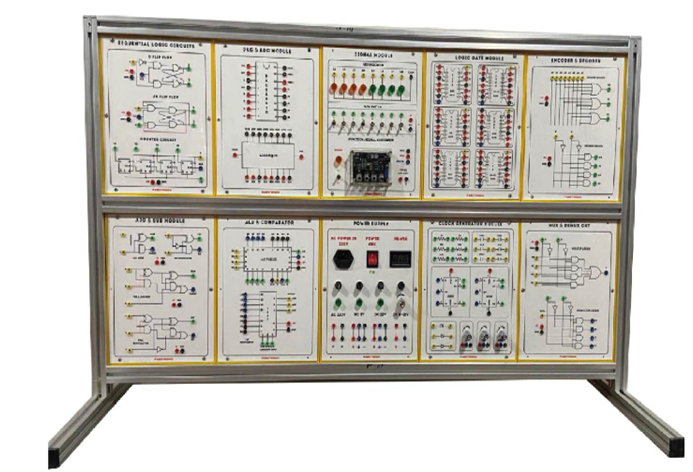
Experiment Modules
- Each of 17 modules is secured in a solid-body plastic housing
2. Each module is equipped with an 8-bit DIP switch for fault simulations. Students can practice trouble shooting by setting the DIP switch to different positions
3. Detailed solutions for the fault simulation are included in the instructor’s manual
4. All sockets on the modules accept 2mm plugs
5. Comprehensive experiment manual and instructor’s manual
6. Module dimension : (255 x 165 x 30)mm
List of Modules
- Diode, Clipper and Clamper Module
2. Rectifier, Differential & Integrator Circuits
3. Transistor Amplification Circuits
4. Field Effect Transistor(FET) Circuits
5. Multistage Amplification Circuits
6. OTL Amplifier Circuit
7. OCL Amplifier & Feedback Circuit
8. Oscillator Circuits(1)
9. Oscillator Circuits(2)
10. Voltage Regulator Circuits
11. Voltage Regulator & Amplitude Modulation(AM) Circuits
12. Frequency Modulation(FM) & OP Amplifier Circuits
13. OP Amplifier Circuits(1)
14. OP Amplifier Circuits(2)
15. OP Amplifier Circuits(3)
16. OP Amplifier Circuits(4)
17. OP Amplifier Circuits(5)
List of Experiments
- Characteristics of Diodes
(1) Silicon diode
(2) Germanium diode
(3) Zener diode
(4) Light emitting diode
(5) Optical diode - Clipping and Clamping Circuits with Diodes
(1) Clipping circuit (1)
(2) Clipping circuit (2)
(3) Clamping circuit (1)
(4) Clamping circuit (2) - Rectifier Circuits
(1) Half wave rectifier circuit
(2) Full wave rectifier circuit
(3) Bridge rectifier circuit
(4) Dual power supply rectifier circuit
(5) Voltage magnified rectifier circuit - Differential and Integrator Circuits
(1) RC direct current charge/discharge circuit
(2) Differential circuit : Square wave input
(3) Differential circuit : Sine wave input
(4) Integrator circuit : Square wave input
(5) Integrator circuit : Sine wave input
(6) RL circuit - Transistors
(1) PNP transistor
(2) NPN transistor - Transistor Amplification Circuits
(1) Common emitter transistor amplification circuit
(2) Common base transistor amplification circuit
(3) Common collector transistor amplification circuit
(4) Switching type transistor circuit
(5) Darlington’s circuit - Field Effect Transistors (FET)
(1) Junction type FET (JFET)
(2) Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor FET (MOSFET) - FET Amplification Circuits
(1) JFET common source amplification circuit : Self-bias
(2) JFET common source amplification circuit : Divide-bias
(3) JFET common drain amplification circuit : Self-bias
(4) JFET common drain amplification circuit : Divide-bias
(5) MOSFET amplification circuit : Biased (1)
(6) MOSFET amplification circuit : Biased (2) - Multi – Stage Amplification Circuits
(1) RC coupled amplification circuit
(2) Direct coupled amplification circuit
(3) Transformer coupled amplification circuit
(4) Push-pull amplification circuit
(5) OTL amplification circuit
(6) OCL amplification circuit
(7) IC amplification circuit - Transistor Negative Feedback Circuits
(1) Serial voltage negative feedback circuit
(2) Parallel voltage negative feedback circuit
(3) Serial current negative feedback circuit
(4) Parallel current negative feedback circuit - Transistor Positive Feedback Circuits
(1) Low-frequency sine wave oscillating circuit
a. RC phase-shifting oscillating circuit
b. Wien bridge oscillating circuit
(2) High-frequency sine wave oscillating circuit
a. Hartley’s oscillating circuit
b. Colpitts oscillating circuit
(3) Crystal oscillating circuit
(4) Astable oscillating circuit
(5) Monostable oscillating circuit
(6) Bistable oscillating circuit
(7) Intermittent oscillating circuit
(8) Schmitt’s oscillating circuit
(9) Sawtooth oscillating circuit - Regulated Voltage/Constant Current Circuits
(1) Regulated voltage circuit with Zener diode
(2) Regulated voltage circuit with Zener diode/transistor
(3) Regulated adjustable voltage circuit
(4) Current-limiting regulated voltage circuit
(5) Regulated voltage circuit with IC
(6) Constant current circuit - Modulation and Demodulation
(1) Amplitude Modulation circuit (AM)
(2) Frequency Modulation circuit (FM)
(3) Amplitude modulation detecting circuit
(4) Frequency demodulation circuit - OP Amplifiers
(1) Transistor differential amplification circuit
(2) Characteristics of OP amplifiers
a. Input impedance measurement
b. Output impedance measurement
c. Bandwidth measurement
d. Slew rate measurement
e. Offset voltage measurement (1)
f . Offset voltage measurement (2) - Basic Characteristics of OP Amplifier
(1) Inverse amplification
(2) Non-Inverse amplification
(3) Voltage-follower circuit
(4) Difference amplification
(5) Sum amplification (Adder)
(6) Clipping circuit
(7) Constant voltage circuit
(8) Constant current circuit
(9) Differentiator circuit
(10) Integrator circuit - Basic Characteristics of OP Amplifier (1) – Negative Feedback
(1) Logarithm amplification circuit
(2) Exponential amplification circuit
(3) Peak value detection circuit
(4) Precision clipping circuit
(5) Voltage adjustment circuit
(6) Sampling/hold circuit
(7) Instrument amplification circuit - Basic Characteristics of OP Amplifier (2) – Negative Feedback
(1) High pass amplification circuit
(2) Low pass amplification circuit
(3) Band pass amplification circuit
(4) RIAA amplification circuit
(5) Tone controller circuit
(6) Single power supply inverse amplification circuit - Basic Characteristics of OP Amplifier – Positive Feedback
(1) Comparator
(2) Schmitt trigger
(3) Window-type comparator
(4) Monostablemultivibrator
(5) Astablemultivibrator
(6) Sine wave oscillation circuit
a. RC oscillator
b. Wien oscillator
Software:
- Built-in circuit simulation of experiment modules.
2. Fault simulation is allowed.
3. Users can flexibly compare the simulation analysis result with hardware signal output.
4. Support virtual instrument.
Accessories
- Experiment Manual and Instructor’s Manual
2. Connection Leads and Plugs
3. Key
4. Storage Cabinet
Additional Accessories:
- Power Cord: 01
- Connecting Wire & Cable
- Complete 5 days Training Included
- User Manual or User Guide
Protection:
Supply and DC Link overvoltage, Phase loss, Drive overload, short circuit, Ground fault, etc.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.